Junctional Epidermolysis Bullosa (JEB1 and JEB2)
Summary
Junctional Epidermolysis Bullosa (JEB), formerly called epitheliogenesis imperfecta (EI) in horses, is an inherited condition affecting the integrity of the skin. Affected horses have fragile skin that blisters easily. Blistering of the mouth and exungulation (loss of the hoof) are also seen. The condition is evident at birth, and foals are typically euthanized in the first few days of life. There is no effective treatment.
Two distinct genetic forms are known. JEB1, resulting from a mutation in LAMC2, is seen in Belgians, while JEB2, resulting from a mutation in LAMA3, is seen in the American Saddlebred.
Date of Last Update: 04/04/2016
JEB1
Back to TopSummary
Junctional Epidermolysis Bullosa (JEB), formerly called epitheliogenesis imperfecta (EI) in horses, is an inherited condition affecting the integrity of the skin. Affected horses have fragile skin that blisters easily. Blistering of the mouth and exungulation (loss of the hoof) are also seen. The condition is evident at birth, and foals are typically euthanized in the first few days of life. There is no effective treatment.
JEB1, resulting from a mutation in LAMC2, is seen in Belgians.
Date of Last Update: 08/02/2016
Results
Understanding the Results
Results of the genetic test for JEB1 are presented as shown below.
| Junctional Epidermolysis Bullosa (JEB1) | ||
|---|---|---|
| N/N | Clear | This horse tested negative for JEB1. |
| N/J1 | Carrier | Both the normal and mutant alleles are present. This horse is positive for the JEB1 mutation but will not develop symptoms. |
| J1/J1 | Affected | This horse carries two copies of the JEB1 mutation and will die of the disease. |
Disease Name and Genes
One of the forms of Junctional Epidermolysis Bullosa (JEB1) is caused by a single-base insertion (1368insC) in the laminin gene LAMC2. The insertion causes a frameshift and premature termination codon at codon position 476, causing the loss of over half of the 1190 amino acids of the LAMC2 protein.
Inheritance
JEB1 is caused by a recessive variant of the LAMC2 gene (LAMC2-1368insC). The recessive allele is commonly abbreviated as J1, with the dominant wild-type allele abbreviated as N.
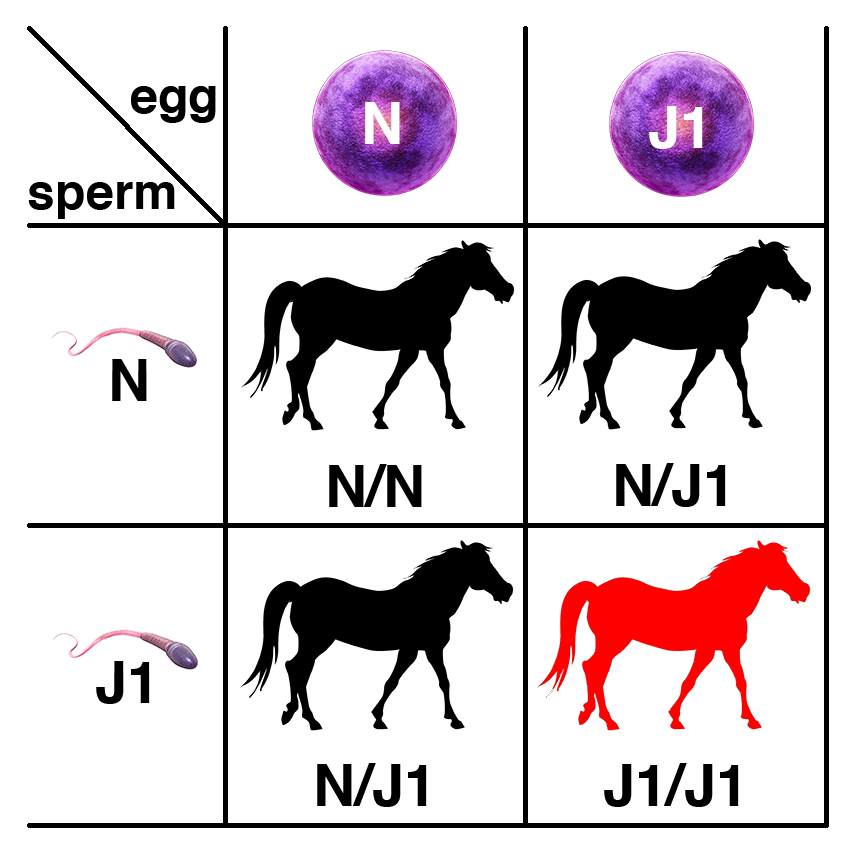
Carriers of the recessive allele (N/J1) have no symptoms of the disease. If two carriers are bred, each foal has a 25% chance of having two copies of the normal allele (N/N), a 50% chance of being a carrier (N/J1), and a 25% chance of being affected (J1/J1).

If a carrier of the recessive allele (N/J1) is bred to a normal horse (N/N), each foal has a 50% chance of having two copies of the normal allele (N/N) and a 50% chance of being a carrier (N/J1).
Citations
JEB2
Back to TopSummary
Junctional Epidermolysis Bullosa (JEB), formerly called epitheliogenesis imperfecta (EI) in horses, is an inherited condition affecting the integrity of the skin. Affected horses have fragile skin that blisters easily. Blistering of the mouth and exungulation (loss of the hoof) are also seen. The condition is evident at birth, and foals are typically euthanized in the first few days of life. There is no effective treatment.
JEB2, resulting from a mutation in LAMA3, is seen in the American Saddlebred.
Date of Last Update: 08/02/2016
Results
Understanding the Results
Results of the genetic test for JEB2 are presented as shown below.
| Junctional Epidermolysis Bullosa (JEB2) | ||
|---|---|---|
| N/N | Clear | This horse tested negative for JEB2. |
| N/J2 | Carrier | Both the normal and mutant alleles are present. This horse is positive for the JEB2 mutation but will not develop symptoms. |
| J2/J2 | Affected | This horse carries two copies of the JEB2 mutation and will die of the disease. |
Disease Name and Genes
One of the forms of Junctional Epidermolysis Bullosa (JEB2) is caused by 6589-bp deletion in the laminin LAMA3 gene. The deletion spans exons 24-27 and results in a nonfunctional laminin 5 protein.
Inheritance
JEB2 is caused by a recessive variant of the LAMA3 gene. The recessive allele is commonly abbreviated as J2, with the dominant wild-type allele abbreviated as N.
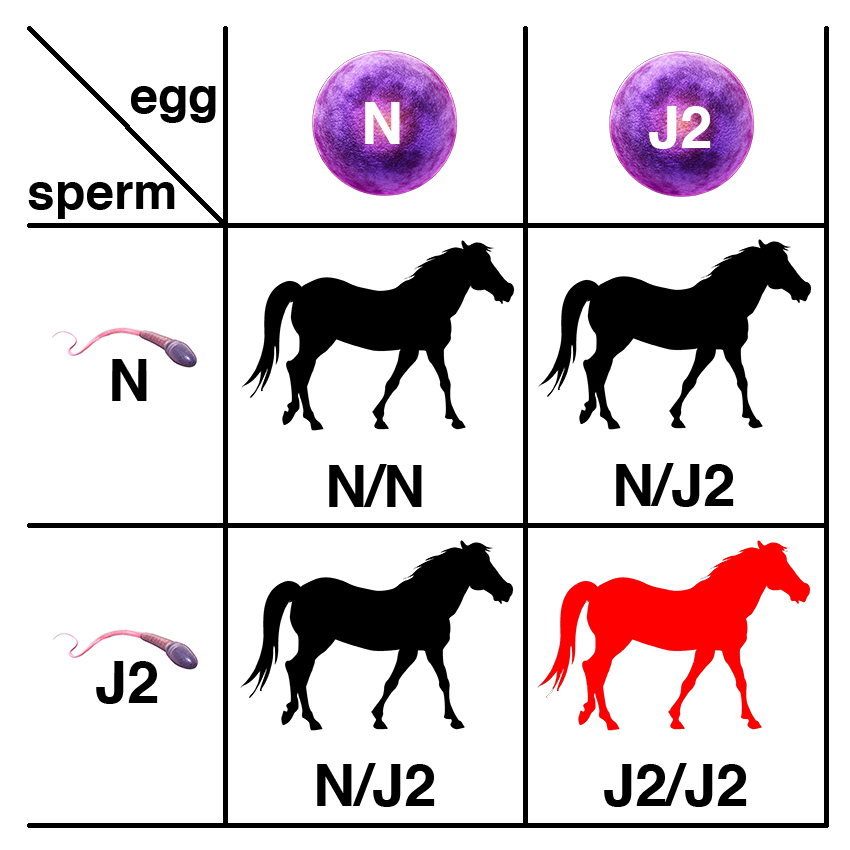
Carriers of the recessive allele (N/J2) have no symptoms of the disease. If two carriers are bred, each foal has a 25% chance of having two copies of the normal allele (N/N), a 50% chance of being a carrier (N/J2), and a 25% chance of being affected (J2/J2).

If a carrier of the recessive allele (N/J2) is bred to a normal horse (N/N), each foal has a 50% chance of having two copies of the normal allele (N/N) and a 50% chance of being a carrier (N/J2).





