| Contents |
|---|
| Warmblood Fragile Foal Syndrome (WFFS) |
| Summary |
| Understanding the Results |
| Disease Name and Genes |
| Inheritance |
Warmblood Fragile Foal Syndrome (WFFS)
Summary
Warmblood Fragile Foal Syndrome (WFFS) is an inherited condition causing thin, fragile skin. Affected foals may be born with skin lesions and an open abdomen and are typically euthanized at birth or within a few days of birth. There is no effective treatment. The condition resembles Ehlers-Danlos syndrome in humans, which has multiple genetic causes. The skin defects resemble those seen in the Hereditary Equine Regional Dermal Asthenia (HERDA), which has a later onset of symptoms. There are also reports of Ehlers-Danlos-like syndromes of unknown origin in a number of breeds.
Warmblood Fragile Foal Syndrome is reported only in Warmbloods. The incidence of carriers is approximately 10%.
Date of Last Update: 08/02/2016
Results
Understanding the Results
Results of the genetic test for Warmblood Fragile Foal Syndrome (WFFS) are presented as shown below.
| Warmblood Fragile Foal Syndrome (WFFS) | ||
|---|---|---|
| N/N | Clear | This horse tested negative for WFFS. |
| N/FFS | Carrier | Both the normal and mutant alleles are present. This horse is positive for the WFFS mutation but will not develop symptoms. |
| FFS/FFS | Affected | This horse carries two copies of the WFFS mutation and will die of the disease. |
Disease Name and Genes
Warmblood Fragile Foal Syndrome (WFFS) results from a G to A substitution that causes the change from Glycine (G) to Arginine (R) at position 678 in the procollagen-lysine, 2-oxoglutarate 5-dioxygenase 1 (PLOD) gene (PLOD-G678R).
Inheritance
Warmblood Fragile Foal Syndrome (WFFS) resulting from the PLOD-G678R variant is recessive. The recessive allele is commonly abbreviated as FFS, with the dominant wild-type allele abbreviated as N.

Carriers of the recessive allele (N/FFS) have no symptoms of the disease. If two carriers are bred, each foal has a 25% chance of having two copies of the normal allele (N/N), a 50% chance of being a carrier (N/FFS), and a 25% chance of being affected (FFS/FFS).
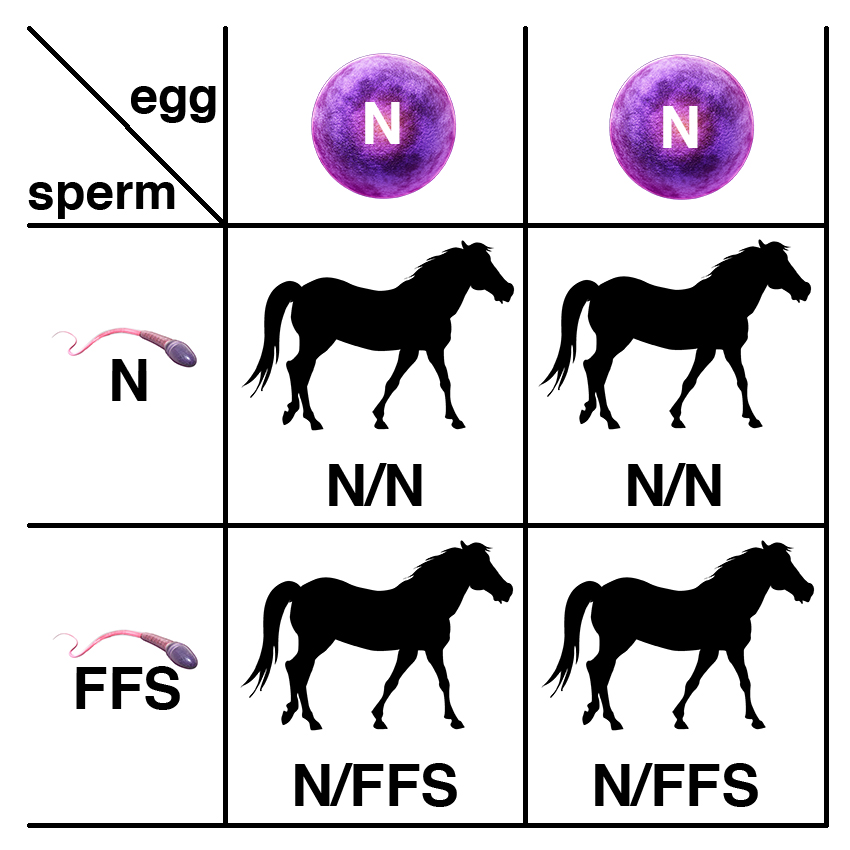
If a carrier of the recessive allele (N/FFS) is bred to a normal horse (N/N), each foal has a 50% chance of having two copies of the normal allele (N/N) and a 50% chance of being a carrier (N/FFS).





